Nutrition and mental health are inseparable in the discourse of good living and sound health. To have a stable mental buildup-up, you need a balanced diet.

The food we eat does not only affect our bodies but our brains as well. In other words, nutrition impacts brain function and overall mental health.
Our brain needs specific nutrients to function optimally, research suggests that deficiencies or imbalances in these nutrients can contribute to mental health challenges.
Learn about the biological connection between nutrition and mental health, as well as what research says are the most essential vitamins to incorporate into your diet and what diets to avoid in order to support your mental health.
The Relationship Between Nutrition and Mental Health

Eating a balanced diet and nutrient-rich food can help to improve mood, increase energy levels and help you think more clearly.
Numerous elements are at play here, from the number of carbohydrates you eat to the way deficiencies in vitamins and minerals affect mental health.
We still have more to learn, but research suggests that the food that one eats influences one’s physical health which subsequently influences mental health.
Effects of Foods on Mental Health
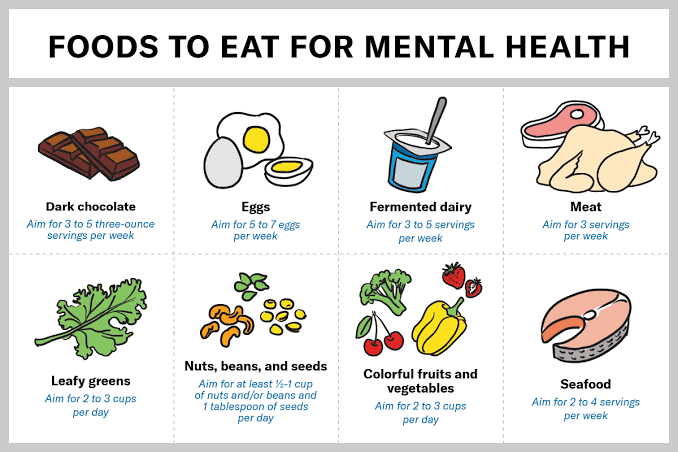
Below are nutrient-rich foods and their effects on one’s mental health:
Carbohydrates
For your brain to be able to concentrate and focus, it requires energy. 20% of all energy needed by the body is used by our brain. This energy comes from blood glucose, and the glucose in our blood comes from the carbohydrates we consume.
When we do not have enough energy for the brain, we can feel weak, tired and unable to think clearly. Making sure you eat regular meals containing some carbohydrates will help with this.
Alongside starchy foods like pasta and rice, sources of carbohydrates are:
- wholegrains
- fruits
- legumes
- vegetables
- lower-fat dairy
When one’s blood glucose rises and falls rapidly, it can have an impact on your mood, making one feel irritable, low, and even triggering symptoms of anxiety.
Keeping your blood glucose levels steady throughout the day is important. Try foods that release energy slowly like oats, cereals, nuts and seeds, and aim to consume smaller portions spaced out throughout the day.
Proteins and Fats
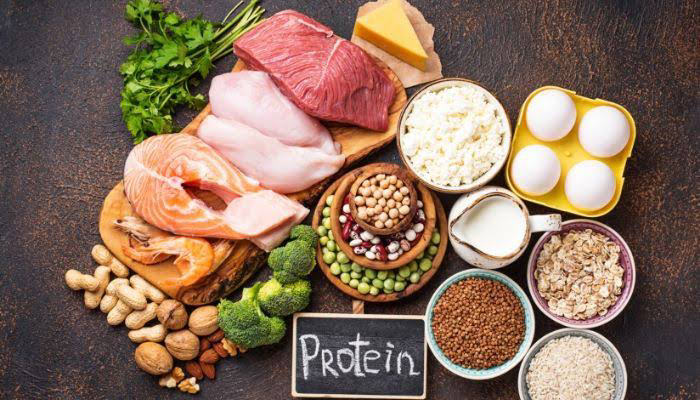

Alongside the energy it gets from carbohydrates, the brain needs amino acids to help regulate thoughts and feelings.
As protein contains amino acids, it’s important to get enough of this in your diet. Protein is found in lean meat, fish, eggs, nuts and seeds, cheese, soya products and legumes.
Some people may be under the impression that all fat is bad for us, but this isn’t the case.
Fatty acids, like omega-3 and omega-6, are essential for our brains to function well.
Healthy fats can be found in nuts, seeds, oily fish, poultry, avocados, dairy products and eggs.
Vitamins and Minerals
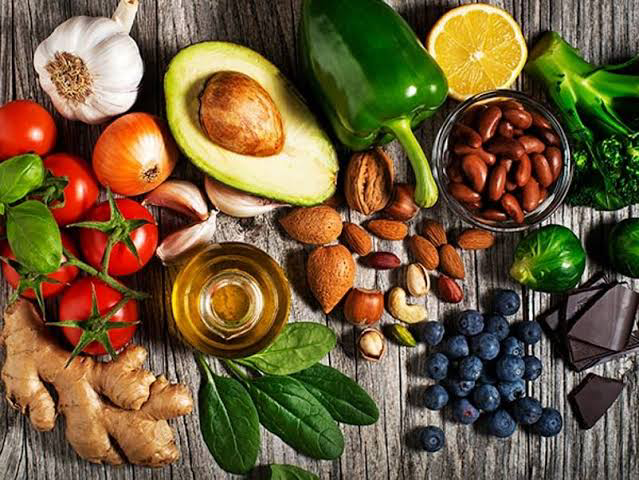

When we do not get enough of certain vitamins and minerals, both our physical and mental health can suffer.
The best way to ensure you’re getting enough of the vitamins and minerals you need is to eat a varied and balanced diet, rich in fruit and vegetables.
For some, a supplement may be needed, but be sure to check this with your doctor or a nutrition professional.
How Can Nutrition Affect Mental Health?
Nutrition affects mental health in a very simple and relatable way.
An instance of this is the constant worry about having enough to eat, and the inability to access nutritious foods can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges.
Bottom Line
It is fully-established that diet plays a fundamental role in health and wellbeing.
Though there is still much to uncover about the underlying relationship between diet and mental health, this post contains compelling evidence that suggests the two are in fact very closely related.
