The versatile Nutrition Blueberries are inexpensive, sweet, and have a gorgeous hue. It can be used for a variety of recipes, including muffins, pies, smoothies, cereal, and salads.
Because of their great nutritional value, potent antioxidant content, and low glycemic carbohydrate content, they are referred to as superfoods.
Most supermarkets have frozen or fresh blueberries, whether they are produced or wild.
Nutrition Information for Blueberries
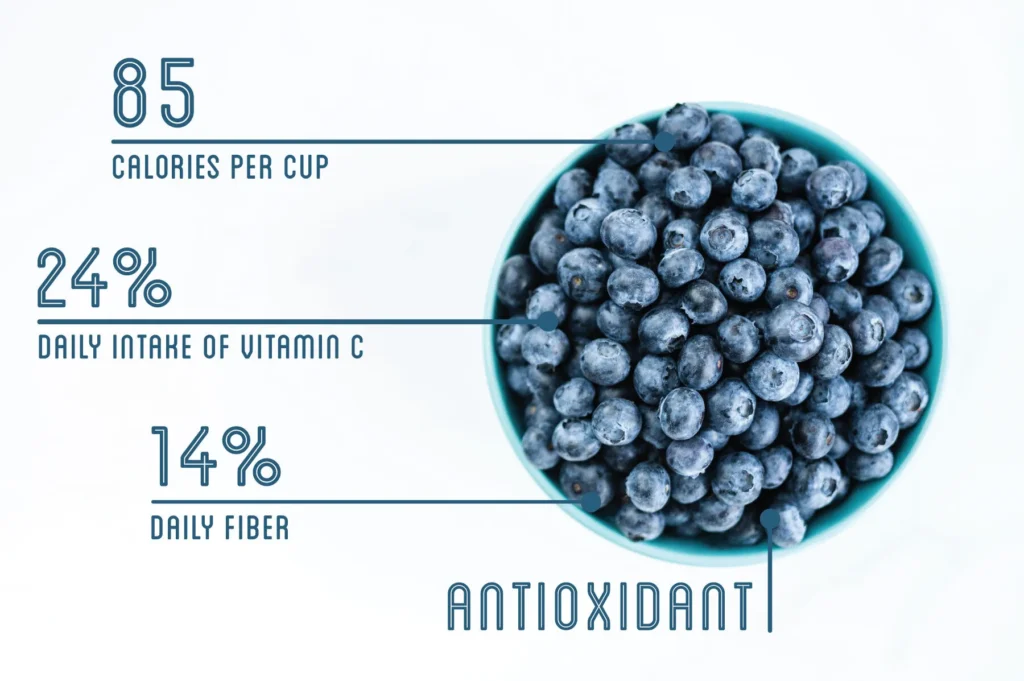
A cup (148g) of raw blueberries has 84 calories, 1g of protein, 21g of carbs, and 0.5g of fat per serving. A great source of manganese, vitamin K, and vitamin C are blueberries. The USDA has given the following dietary data for the Nutrition Blueberries.
Blueberries Health Benefits
Polyphenols, found in blueberries, are substances that are kind of an all-around health star. Because Nutrition Blueberries contain numerous micronutrients, scientists have discovered numerous advantages to them. Eating a one-third cup of blueberries per day has been linked in studies to a lower risk of illness.
Boost Memory Retention
It has been demonstrated that blueberries can aid preserve memory and stave off cognitive decline.
According to a tiny study, people who drank blueberry juice regularly performed better on memory tests and showed fewer signs of depression. Berries have been shown in a much larger, longer-term study to postpone cognitive aging by up to 2.5 years (published in 2012).
Combat Inflammation
There are lots of phyto (plant) components in blueberries. Among these are flavonoids, which give berries their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. There’s no denying that blueberries are a great source of vitamin C, an antioxidant that boosts immunity, promotes wound healing, and has anti-aging qualities.
Lower Your Risk of Heart Attack
According to one study, women who had three or more servings of berries per week, such as blueberries, had a 32% lower risk of heart attacks.
One reason a Nutrition Blueberries are so good is that they are high in satiating, heart-healthy fiber. The indigestible portion of carbohydrates called fiber helps control blood sugar, regulates bowel movements, promotes satiety, and keeps cholesterol away from the heart.
Antioxidants called anthocyanins, which are also found in blueberries, may protect the heart by enhancing blood flow and preventing plaque formation.
Reduce the Risk of Cancer
Eating foods high in anthocyanins may also help prevent cancer, according to some research. Blueberries and other vividly colored fruits and vegetables contain anthocyanins, a kind of flavonoid.
Boost Your Sensitivity to Insulin
Nutrition Blueberries do naturally contain sugars, however, their anthocyanins seem to help decrease blood sugar and enhance insulin sensitivity. Thus, they may be able to reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.

Allergies to Blueberries
Since salicylates are a naturally occurring component of blueberries and are also present in other foods and personal care items, you should use caution while consuming blueberries if you have an allergy to these chemicals. Aspirin is also made of salicylates.
Adverse Results
Certain drugs may interact with blueberries. Blueberries are rich in vitamin K, which is crucial for blood clotting, in addition to salicylates, which function as a natural blood thinner. Consult your doctor about the consequences of consuming foods high in salicylates and vitamin K on your blood thinner, such as Coumadin (warfarin).
Different Blueberry Varieties
One of the rare fruits that grows naturally in North America is the blueberry. Either cultivated or wild blueberries are available for purchase. Compared to their farmed siblings, wild berries are smaller and have a stronger, tangier flavor. In addition, they have more antioxidant content than farmed berries.
Blueberries are available both fresh and frozen, and both are nutrient-dense. Berries that are frozen are always a sensible choice because they are typically harvested at their prime and last longer than fresh berries.

When Is It Best To Eat Blueberries?
While South American imports, where the seasons are reversed, are available from October to March, North American blueberries are harvested from April to September.
Select bright blueberries that are firm, dry, spherical, have smooth skin, and appear slightly frosted. You can use reddish blueberries in cooking, but they aren’t ripe and won’t ripen once harvested.
Steer clear of berries that are shriveled, squishy, or show any indication of mold.
When they’re not in season, fresh blueberries can be one of the more costly fruits. Flash-frozen blueberries are an affordable and nutritious alternative.
They work well in smoothies, baked products, and even as a topping for overnight oats. Berries that are frozen are often harvested at their most nutritious stage, known as peak ripeness, and freezing helps maintain their nutritional value.
Food Safety and Storage
Fresh blueberries should be refrigerated and consumed within ten days. Before eating, they should be washed under running water, but you should wait to wash them until right before you eat them or cook them with blueberries.
For optimal quality, freeze-till-use frozen blueberries last up to a year, but they can be safely used before then.
How to Prepare Blueberries
Blueberries are very versatile and work well in pies, crumbles, muffins, and pancakes. They can be mixed into smoothies or eaten with oatmeal, cottage cheese, and yogurt. They even work nicely as a savory sauce when combined with balsamic vinegar. Add them to a salad for a vibrant and energizing touch, or eat them by themselves as a delectable snack.

The Bottom Line
Blueberries are very nourishing and healthful. They improve the health of your heart, brain, and many other body systems.
They’re also colorful, sweet, and convenient to eat frozen or fresh.
